extramask
Σπουδαίος
- Εγγρ.
- 3 Ιαν 2009
- Μηνύματα
- 728
- Κριτικές
- 50
- Like
- 163
- Πόντοι
- 3.285
Ανακάλυψα τυχαία ένα άρθρο στην ιστοσελίδα του The Economist που αναφέρεται στον τρόπο με τον οποίο οι νέες τεχνολογίες (δηλαδή το internet) έχουν επηρεάσει τον τρόπο που λειτουργεί η βιομηχανία του σεξ. Είναι αρκετά μεγάλο άρθρο αλλά αξίζει να το διαβάσει κανείς αν έχει χρόνο. Εν ολίγοις λέει πως λόγω του ότι πλέον το internet παίζει μεγάλο ρόλο στον τρόπο με τον οποίο δουλεύουν οι ιερόδουλες, υπάρχει πτώση των τιμών και αναβάθμιση των υπηρεσιών. Αναφέρεται επίσης σε άλλους παράγοντες που παίζουν ρόλο στις τιμές κατά τόπους, όπως μετανάστευση, ιδιαιτερότητες της τοπικής αγοράς, εξωτερική εμφάνιση, κτλ. Θα παραθέσω τα γραφήματα του άρθρου τα οποία βρήκα ενδιαφέροντα
Παρακάτω είναι το κείμενο και το link
FOR those seeking commercial sex in Berlin, Peppr, a new app, makes life easy. Type in a location and up pops a list of the nearest prostitutes, along with pictures, prices and physical particulars. Results can be filtered, and users can arrange a session for a €5-10 ($6.50-13) booking fee. It plans to expand to more cities.
Peppr can operate openly since prostitution, and the advertising of prostitution, are both legal in Germany. But even where they are not, the internet is transforming the sex trade. Prostitutes and punters have always struggled to find each other, and to find out what they want to know before pairing off. Phone-box “tart cards” for blonde bombshells and leggy señoritas could only catch so many eyes. Customers knew little about the nature and quality of the services on offer. Personal recommendations, though helpful, were awkward to come by. Sex workers did not know what risks they were taking on with clients.
Now specialist websites and apps are allowing information to flow between buyer and seller, making it easier to strike mutually satisfactory deals. The sex trade is becoming easier to enter and safer to work in: prostitutes can warn each other about violent clients, and do background and health checks before taking a booking. Personal web pages allow them to advertise and arrange meetings online; their clients’ feedback on review sites helps others to proceed with confidence.
Even in places such as America, where prostitution and its facilitation are illegal everywhere except Nevada, the marketing and arrangement of commercial sex is moving online. To get round the laws, web servers are placed abroad; site-owners and users hide behind pseudonyms; and prominently placed legalese frames the purpose of sites as “entertainment” and their content as “fiction”.
The shift online is casting light on parts of the sex industry that have long lurked in the shadows. Streetwalkers have always attracted the lion’s share of attention from policymakers and researchers because they ply their trade in public places. They are more bothersome for everyone else—and, because they are the most vulnerable, more likely to come to the attention of the police and of social or health workers. But in many rich countries they are a minority of all sex workers; just 10-20% in America, estimates Ronald Weitzer, a sociologist at George Washington University.
The wealth of data available online means it is now possible to analyse this larger and less examined part of the commercial-sex market: prostitution that happens indoors. It turns out to be surprisingly similar to other service industries. Prostitutes’ personal characteristics and the services they offer influence the prices they charge; niche services attract a premium; and the internet is making it easier to work flexible hours and to forgo a middleman.
Websites such as AdultWork allow prostitutes, both those working independently and those who work through agencies and brothels, to create profiles through which customers can contact them. They can upload detailed information about themselves, the range of services they provide, and the rates they charge. Clients can browse by age, bust or dress size, ethnicity, sexual orientation or location.
Other websites garner information from clients, who upload reviews of the prostitutes they have visited with details of the services offered, prices paid and descriptions of the encounters. On PunterNet, a British site, clients describe the premises, the encounter and the sex worker, and choose whether to recommend her. Such write-ups have enabled her to build a personal brand, says one English escort, Michelle (like many names in this article, a pseudonym), and to attract the clients most likely to appreciate what she offers.
TrickAdvisor
We have analysed 190,000 profiles of sex workers on an international review site. (Since it is active in America, it was not willing to be identified for this article. A disclaimer on the site says the contents are fictional; we make the assumption that they are informative all the same.) Each profile includes customers’ reviews of the worker’s physical characteristics, the services they offer and the price they charge.
The data go back as far as 1999. For each individual we have used the most recent information available, with prices corrected for inflation. Some of those featured may appear under more than one name, or also work through agencies. The data cover 84 cities in 12 countries, with the biggest number of workers being in America and most of the rest in big cities in other rich countries. As this site features only women, our analysis excludes male prostitutes (perhaps a fifth of the commercial-sex workforce). Almost all of those leaving reviews are men.
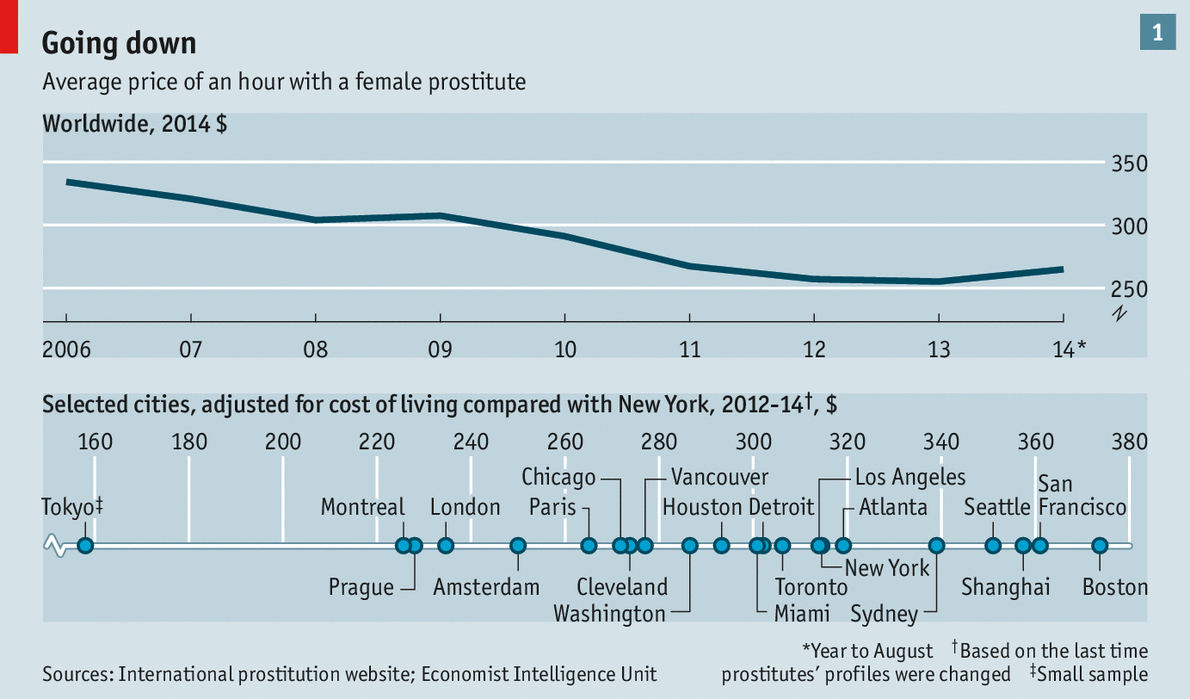
The most striking trend our analysis reveals is a drop in the average hourly rate of a prostitute in recent years (see chart 1). One reason is surely the downturn that followed the 2007-08 financial crisis. Even prostitutes working in places that escaped the worst effects have been hit. Vanessa, a part-time escort in southern England, finds that weeks can go by without her phone ringing. Men see buying sex as a luxury, she says, and with the price of necessities rising it is one they are cutting back on. Even when she offers discounts to whip up interest, clients are scarcer than they were. In places where the job market slumped, the effect is more marked (whether prostitution is legal may affect prices, too, but the wide variation between American cities shows that this is not the only factor). The cost of an hour with an escort in Cleveland, Ohio, where unemployment peaked at 12.5% in 2010, has tumbled.
Large-scale migration is another reason prices are falling. Big, rich cities are magnets for immigrants of all professions, including sex workers. Nick Mai of London Metropolitan University has studied foreign sex workers in Britain. He has found that as they integrate and get used to the local cost-of-living, their rates tend to rise. But where the inward flow is unceasing, or where the market was previously very closed, immigrants can push prices down.
Since the European Union enlarged to include poorer eastern European countries, workers of every sort have poured into their richer neighbours. By all accounts prices have been dropping in Germany as a result of the arrival of new, poor migrants, says Rebecca Pates of the University of Leipzig. Sally, a semi-retired British escort who runs a flat in the west of England where a few “mature” women sell sex, says English girls are struggling to find work: there are too many eastern European ones willing to accept less.
Twenty years ago most prostitutes in Norway were locals who all aimed to charge about the same, says May-Len Skilbrei, a sociologist at Oslo University. Today, with growing numbers of sex workers from the Baltic states and central Europe, as well as Nigerians and Thais, such unofficial price controls are harder to sustain.
Inexperience is another reason newcomers to prostitution may underprice themselves, at least at first. Maxine Doogan, an American prostitute and founder of the Erotic Service Providers Union, a lobby group, learnt her trade from a woman who worked for years in a brothel in Nevada, the only American state where prostitution is legal. The older woman taught her what to regard as standard or extra, and how much to charge. When Ms Doogan started out, in 1988, standard services (vaginal sex and fellatio) cost $200 an hour, the equivalent of $395 today. But some of those starting out now still charge $200, she says, or offer extra services, including risky ones such as oral sex without a condom, without charging an appropriate premium.
The shift online has probably boosted supply by drawing more locals into the sex trade, too. More attractive and better-educated women, whose marital and job prospects are therefore better, are more likely to consider sex work if it is arranged online. Indoor sex work is safer than streetwalking, and the risk of arrest is lower. Rented flats or hotel rooms are more discreet than brothels, so family and friends are less likely to identify the new source of income. Anonymity becomes a possibility, which lessens the fear of stigma. Creating an online profile separates the decision to take up the work from parading for punters.
Meanwhile, broader social change may be reducing demand—and thus, prices. Free, no-strings-attached sex is far easier to find than in the past. Apps such as Tinder facilitate speedy hookups; websites such as Ashley Madison and Illicit Encounters, adulterous ones. Greater acceptance of premarital intercourse and easier divorce mean fewer frustrated single and married men turning to prostitutes.
Dearer for johns
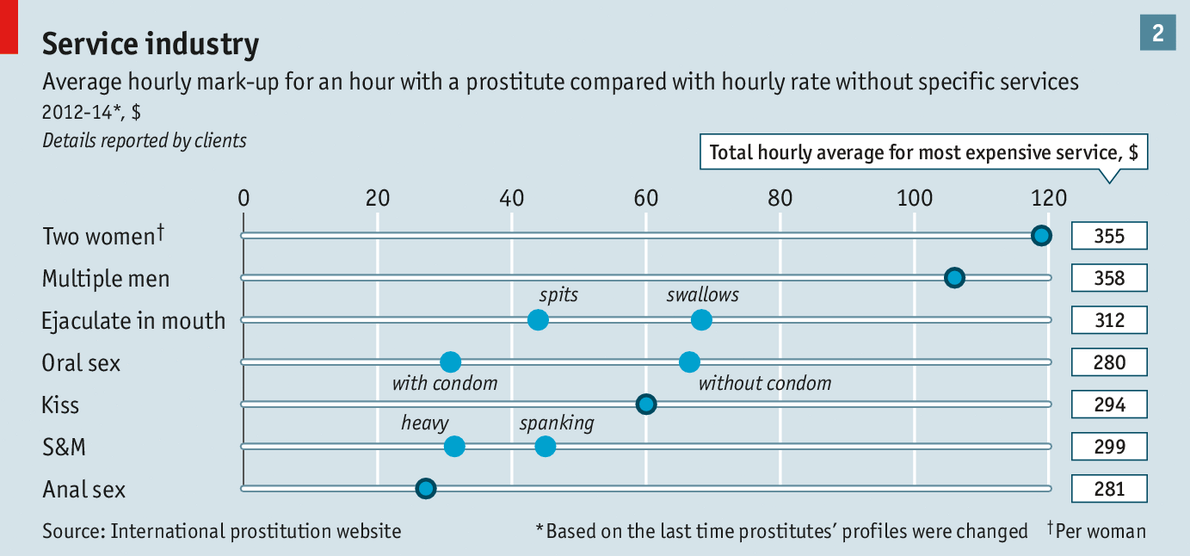
Our analysis shows how a prostitute’s hourly rate varies according to the nature of the services she provides and her reported physical characteristics. As in other bits of the economy, clients who seek niche services must pay more. Sex workers who offer anal sex or spanking earn on average $25 or $50 more per hour, respectively (see chart 2). Those who will accept two male clients at once or do threesomes with another woman command a larger premium.
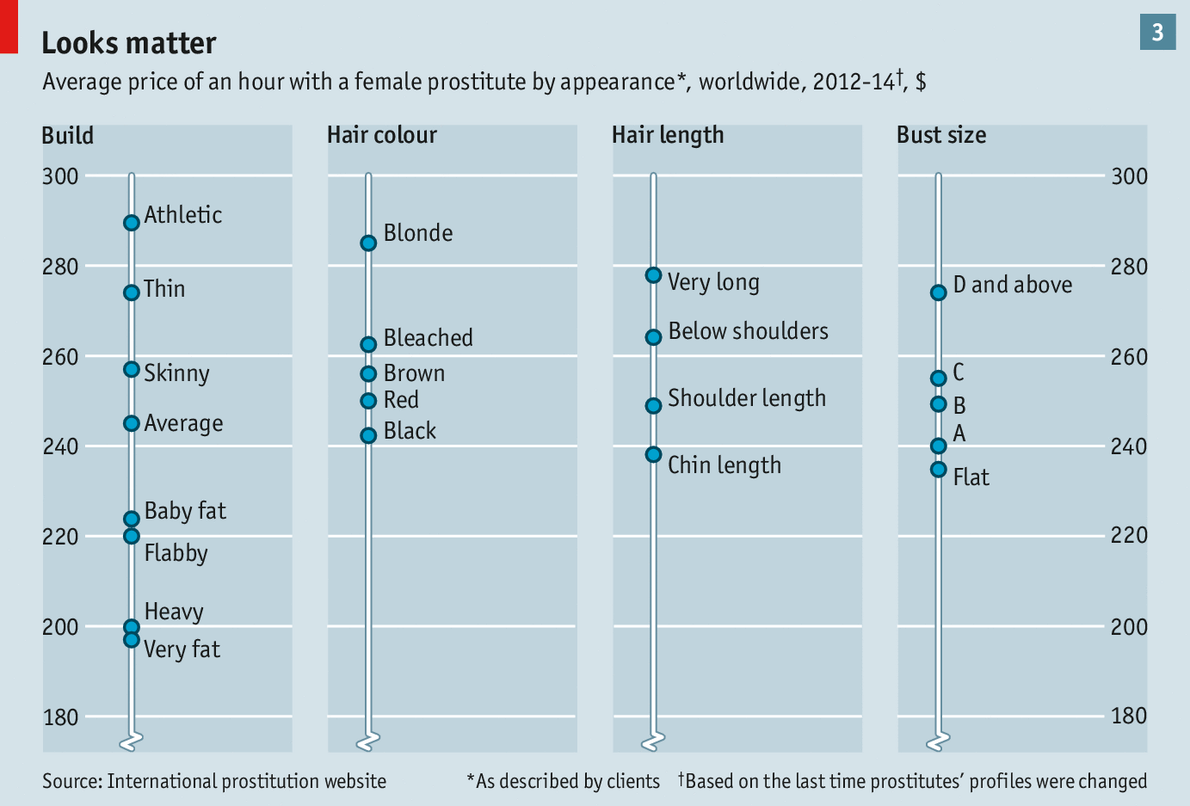
Appearance matters a great deal. The customers who reported encounters to the website we analysed clearly value the stereotypical features of Western beauty: women they describe as slim but not scrawny, or as having long blonde hair or full breasts, can charge the highest hourly rates (see chart 3). Hair that is bleached too unconvincingly to be described as blonde attracts a lower premium, but is still more marketable than any other colour. For those not naturally well endowed, breast implants may make economic sense: going from flat-chested to a D-cup increases hourly rates by approximately $40, meaning that at a typical price of $3,700, surgery could pay for itself after around 90 hours. The 12% share of women featured on the site who are described both as athletic, slim or thin, and as being at least a D-cup, suggests that quite a few have already taken this route.
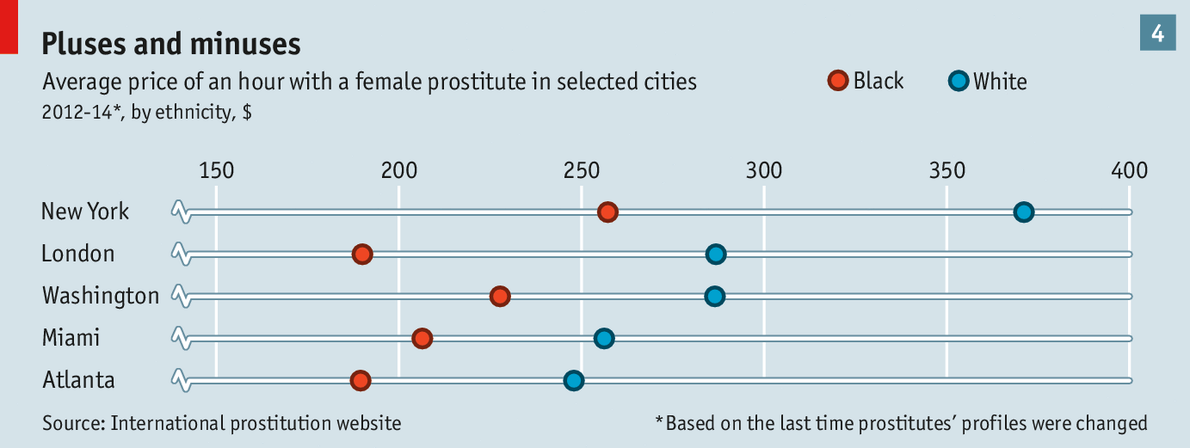
A prostitute’s rates also vary according to her ethnicity and nationality. What attracts a premium in one place can attract a penalty in another. According to our analysis, in four big American cities and London, black women earn less than white ones (see chart 4).
We had too few data from other cities for a reliable breakdown by ethnicity. But Christine Chin of the American University in Washington, DC, has studied high-end transnational prostitutes in several countries. In Kuala Lumpur, she found, black women command very high rates and in Singapore, Vietnamese ones do. In Dubai, European women earn the most. What counts as exotic and therefore desirable varies from place to place, and depends on many factors, such as population flows.
Local markets have other quirks. According to the site we analysed, an hour with an escort in Tokyo is a bargain compared with one in London or New York. Yet a cost-of-living index compiled by the Economist Intelligence Unit, our sister organisation, suggests that Tokyo is the most expensive city overall of the three. The apparent anomaly may be because escorts who appear on an English-language review site mostly cater to foreigners, who are not offered the more unusual—and expensive—services Japanese prostitutes provide for locals. These include the bubble baths and highly technical massages of Sopurando (“Soapland”), a red-light district in Tokyo, which can cost ¥60,000 ($600) for a session and involve intercourse (although that is not advertised).
A degree appears to raise earnings in the sex industry just as it does in the wider labour market. A study by Scott Cunningham of Baylor University and Todd Kendall of Compass Lexecon, a consultancy, shows that among prostitutes who worked during a given week, graduates earned on average 31% more than non-graduates. More lucrative working patterns rather than higher hourly rates explained the difference. Although sex workers with degrees are less likely to work than others in any given week (suggesting that they are more likely to regard prostitution as a sideline), when they do work they see more clients and for longer. Their clients tend to be older men who seek longer sessions and intimacy, rather than a brief encounter.
How much brothels and massage parlours use the internet depends on local laws. America’s legal restrictions mean that they keep a low profile, both offline and online. In Britain, where brothels are illegal though prostitution is not, massage parlours advertise the rotas and prices of their workers online but are coy about the services rendered. By contrast Paradise, a mega-brothel in Germany, boasts a frank and informative website.
But it is independent sex workers for whom the internet makes the biggest difference. Mr Cunningham has tracked the number of sex workers in American cities on one review site. In the decade to 2008, during which online advertising for commercial sex took off, the share describing themselves as independent grew.
For prostitutes, the internet fulfils many of the functions of a workplace. It is a “break-room and hiring hall”, says Melissa Gira Grant, the author of “Playing the Whore: The Work of Sex Work”. Online forums replace the office water-cooler. Women exchange tips on dealing with the everyday challenges of sex work; a busy thread on one forum concerns which sheets stand up best to frequent washing.
A mother in Scotland asks how other prostitutes juggle child care and selling sex, given that bookings are often made at short notice so babysitters are hard to arrange. Another contributor who is thinking of having children asks how much other women saved before taking time off to have a baby, and whether the new calls on their time meant they earned less after giving birth. One reply points out that prostitution is easier than many other jobs to combine with motherhood: it pays well enough to cover child-care costs, and can be fitted around school holidays, plays and sports days, and children’s illnesses.
Women who are considering entering the industry often seek advice online from those already in it before making up their minds. Melanie, who earns £65,000 ($109,000) a year, says that she is considering selling sex on the side for a few months to pay off debts. She asks which agency to use and how to get the highest rate. But she also worries that a stint selling sex would harm her future career. Experienced sex workers respond that anonymity will be easier to preserve if she works independently, rather than through an agency, and warn her that she is entering a crowded market. The stress of living a double life should not be underestimated, they caution, and it will not be easy money.
Many of those contributing to such discussions hold other jobs, often part-time, and tout the merits of a steady source of additional income and something innocuous to put on a CV. Sarah says her escort work means she can pay for her daughter’s dance and music lessons, which would be unaffordable on just her “civvy job”. Some husbands and boyfriends know about their wives’ and girlfriends’ work, or even act as managers, drivers and security. Other women keep what they do a secret from those closest to them.
Advertising and booking clients online give prostitutes flexibility about where to work. They can “tour”, using their own home pages or profiles on specialist websites to advertise where they will be and when. In densely populated Britain, where prostitutes work in most places, tours allow those who normally serve small towns to visit cities crammed with potential customers. In Norway, says Ms Skilbrei, prostitutes are concentrated in the main cities, so a tour is a chance to satisfy pent-up demand in small towns.
The freelancers, part-timers and temps the internet is bringing to the sex trade are likely to help it absorb demand shocks. In 2008 the Republican and Democratic national conventions were held in Minneapolis and Denver respectively. Around 50,000 visitors flocked to each city. Another study by Mr Cunningham and Mr Kendall found that the numbers of advertisements for sex on the now-defunct “erotic services” section of Craigslist, a classified-advertising site, were 41% higher in Minneapolis and 74% higher in Denver around the conventions than expected for those days of the week and times of year.
Health and safety
Sex work exposes those who do it to serious risks: of rape and other violence, and of sexually transmitted infections. But in this industry, like many others, the internet is making life easier.
Online forums allow prostitutes to share tips about how to stay safe and avoid tangling with the law. Some sites let them vouch for clients they have seen, improving other women’s risk assessments. Others use services such as Roomservice 2000, another American site, where customers can pay for a background check to present to sex workers. Both sides benefit since the client can demonstrate trustworthiness without giving credit-card details or phone numbers to the prostitute.
Sites that are active in restrictive jurisdictions must be careful not to fall foul of the law. In June the FBI shut down MyRedBook, an advertising-and-review site with a chat section for sex workers. Its owners face charges of money laundering and facilitating prostitution. American police sometimes use such sites to entrap prostitutes. As they wise up to this, sex workers are using sites that allow them to verify clients’ identities to help them avoid stings. But that adds unnecessary hassle and distracts from what should be most important: staying safe. “Screening for cops [is now] the priority over screening for rapists, thieves, kidnappers,” says Ms Doogan.
In Britain, Ugly Mugs runs an online database that prostitutes can use to check punters’ names and telephone numbers. In America the National Blacklist, a “deadbeat registry”, allows them to report men who are abusive or fail to pay. Other women can check potential clients by names, telephone numbers, e-mail addresses and online aliases. Though not specifically aimed at sex workers, apps such as Healthvana make it easy for buyer and seller to share verified results in sexual-health tests.
Moving online means prostitutes need no longer rely on the usual intermediaries—brothels and agencies; pimps and madams—to drum up business or provide a venue. Some will decide to go it alone. That means more independence, says Ana, a Spanish-American erotic masseuse who works in America and Britain. It also means more time, effort and expertise put into marketing. “You need a good website, lots of great pictures, you need to learn search-engine optimisation…it’s exhausting at times,” she says.
Leaving the streets behind
Others will still prefer to have a manager or assistant to take care of bookings and social media. “[Nowadays] you have people hitting you up on Twitter, Facebook, your website, and e-mail,” says Ms Doogan. Eros.com, an international listings site, allows prostitutes to tell clients whether they are currently available. But it means going online every hour or two, which is a chore. And online advertising is not cheap. Ms Doogan used to spend 10% of her income on print adverts; she spends far more on online ones because with so many people advertising, returns are lower. Checking customers’ bona fides also takes time.
Meanwhile some traditional forms of prostitution are struggling. In the decade to 2010 the number of licensed sex clubs in the Netherlands fell by more than half, according to a study for Platform31, a Dutch research network. Much of the decline will have been offset by the growth of sex work advertised online, it reckons. Many prostitutes would rather work from private premises than in a club or for an agency, says Sietske Altink, one of the authors. Dutch municipalities often bar such work—but the option of finding clients online makes such rules harder to enforce.
That shift will make the sex industry harder for all governments to control or regulate, whether they seek to do so for pragmatic or moralistic reasons, or out of concern that not all those in the industry are there by their own free will. Buyers and sellers of sex who strike deals online are better hidden and more mobile than those who work in brothels, or from clubs or bars, points out Professor Weitzer of George Washington University. Ireland has banned the advertising of sexual services since 1994. The prohibition has achieved almost nothing, says Graham Ellison, a sociologist at Queen’s University in Belfast. Websites simply moved to other jurisdictions. The closure of those such as MyRedBook may prompt American ones to do the same; as they grow more specialised, the excuse that they merely host classified advertisements is wearing thin.
In the long term there will always be people who, for whatever reason, want to hire a prostitute rather than do without sex or pick up a partner in a bar. As paid-for sex becomes more readily and discreetly available online, more people will buy it. A greater awareness may develop that not all sex workers are the victims of exploitation. The very discretion—and the hidden nature of such prostitution—may also mean that the stigma persists. But, overall, sex workers will profit. The internet has disrupted many industries. The oldest one is no exception.
www.economist.com/news/briefing/21611074-how-new-technology-shaking-up-oldest-business-more-bang-your-buck]http://www.economist.com/news/briefing/21611074-how-new-technology-shaking-up-oldest-business-more-bang-your-buck[/url]




Παρακάτω είναι το κείμενο και το link
FOR those seeking commercial sex in Berlin, Peppr, a new app, makes life easy. Type in a location and up pops a list of the nearest prostitutes, along with pictures, prices and physical particulars. Results can be filtered, and users can arrange a session for a €5-10 ($6.50-13) booking fee. It plans to expand to more cities.
Peppr can operate openly since prostitution, and the advertising of prostitution, are both legal in Germany. But even where they are not, the internet is transforming the sex trade. Prostitutes and punters have always struggled to find each other, and to find out what they want to know before pairing off. Phone-box “tart cards” for blonde bombshells and leggy señoritas could only catch so many eyes. Customers knew little about the nature and quality of the services on offer. Personal recommendations, though helpful, were awkward to come by. Sex workers did not know what risks they were taking on with clients.
Now specialist websites and apps are allowing information to flow between buyer and seller, making it easier to strike mutually satisfactory deals. The sex trade is becoming easier to enter and safer to work in: prostitutes can warn each other about violent clients, and do background and health checks before taking a booking. Personal web pages allow them to advertise and arrange meetings online; their clients’ feedback on review sites helps others to proceed with confidence.
Even in places such as America, where prostitution and its facilitation are illegal everywhere except Nevada, the marketing and arrangement of commercial sex is moving online. To get round the laws, web servers are placed abroad; site-owners and users hide behind pseudonyms; and prominently placed legalese frames the purpose of sites as “entertainment” and their content as “fiction”.
The shift online is casting light on parts of the sex industry that have long lurked in the shadows. Streetwalkers have always attracted the lion’s share of attention from policymakers and researchers because they ply their trade in public places. They are more bothersome for everyone else—and, because they are the most vulnerable, more likely to come to the attention of the police and of social or health workers. But in many rich countries they are a minority of all sex workers; just 10-20% in America, estimates Ronald Weitzer, a sociologist at George Washington University.
The wealth of data available online means it is now possible to analyse this larger and less examined part of the commercial-sex market: prostitution that happens indoors. It turns out to be surprisingly similar to other service industries. Prostitutes’ personal characteristics and the services they offer influence the prices they charge; niche services attract a premium; and the internet is making it easier to work flexible hours and to forgo a middleman.
Websites such as AdultWork allow prostitutes, both those working independently and those who work through agencies and brothels, to create profiles through which customers can contact them. They can upload detailed information about themselves, the range of services they provide, and the rates they charge. Clients can browse by age, bust or dress size, ethnicity, sexual orientation or location.
Other websites garner information from clients, who upload reviews of the prostitutes they have visited with details of the services offered, prices paid and descriptions of the encounters. On PunterNet, a British site, clients describe the premises, the encounter and the sex worker, and choose whether to recommend her. Such write-ups have enabled her to build a personal brand, says one English escort, Michelle (like many names in this article, a pseudonym), and to attract the clients most likely to appreciate what she offers.
TrickAdvisor
We have analysed 190,000 profiles of sex workers on an international review site. (Since it is active in America, it was not willing to be identified for this article. A disclaimer on the site says the contents are fictional; we make the assumption that they are informative all the same.) Each profile includes customers’ reviews of the worker’s physical characteristics, the services they offer and the price they charge.
The data go back as far as 1999. For each individual we have used the most recent information available, with prices corrected for inflation. Some of those featured may appear under more than one name, or also work through agencies. The data cover 84 cities in 12 countries, with the biggest number of workers being in America and most of the rest in big cities in other rich countries. As this site features only women, our analysis excludes male prostitutes (perhaps a fifth of the commercial-sex workforce). Almost all of those leaving reviews are men.
The most striking trend our analysis reveals is a drop in the average hourly rate of a prostitute in recent years (see chart 1). One reason is surely the downturn that followed the 2007-08 financial crisis. Even prostitutes working in places that escaped the worst effects have been hit. Vanessa, a part-time escort in southern England, finds that weeks can go by without her phone ringing. Men see buying sex as a luxury, she says, and with the price of necessities rising it is one they are cutting back on. Even when she offers discounts to whip up interest, clients are scarcer than they were. In places where the job market slumped, the effect is more marked (whether prostitution is legal may affect prices, too, but the wide variation between American cities shows that this is not the only factor). The cost of an hour with an escort in Cleveland, Ohio, where unemployment peaked at 12.5% in 2010, has tumbled.
Large-scale migration is another reason prices are falling. Big, rich cities are magnets for immigrants of all professions, including sex workers. Nick Mai of London Metropolitan University has studied foreign sex workers in Britain. He has found that as they integrate and get used to the local cost-of-living, their rates tend to rise. But where the inward flow is unceasing, or where the market was previously very closed, immigrants can push prices down.
Since the European Union enlarged to include poorer eastern European countries, workers of every sort have poured into their richer neighbours. By all accounts prices have been dropping in Germany as a result of the arrival of new, poor migrants, says Rebecca Pates of the University of Leipzig. Sally, a semi-retired British escort who runs a flat in the west of England where a few “mature” women sell sex, says English girls are struggling to find work: there are too many eastern European ones willing to accept less.
Twenty years ago most prostitutes in Norway were locals who all aimed to charge about the same, says May-Len Skilbrei, a sociologist at Oslo University. Today, with growing numbers of sex workers from the Baltic states and central Europe, as well as Nigerians and Thais, such unofficial price controls are harder to sustain.
Inexperience is another reason newcomers to prostitution may underprice themselves, at least at first. Maxine Doogan, an American prostitute and founder of the Erotic Service Providers Union, a lobby group, learnt her trade from a woman who worked for years in a brothel in Nevada, the only American state where prostitution is legal. The older woman taught her what to regard as standard or extra, and how much to charge. When Ms Doogan started out, in 1988, standard services (vaginal sex and fellatio) cost $200 an hour, the equivalent of $395 today. But some of those starting out now still charge $200, she says, or offer extra services, including risky ones such as oral sex without a condom, without charging an appropriate premium.
The shift online has probably boosted supply by drawing more locals into the sex trade, too. More attractive and better-educated women, whose marital and job prospects are therefore better, are more likely to consider sex work if it is arranged online. Indoor sex work is safer than streetwalking, and the risk of arrest is lower. Rented flats or hotel rooms are more discreet than brothels, so family and friends are less likely to identify the new source of income. Anonymity becomes a possibility, which lessens the fear of stigma. Creating an online profile separates the decision to take up the work from parading for punters.
Meanwhile, broader social change may be reducing demand—and thus, prices. Free, no-strings-attached sex is far easier to find than in the past. Apps such as Tinder facilitate speedy hookups; websites such as Ashley Madison and Illicit Encounters, adulterous ones. Greater acceptance of premarital intercourse and easier divorce mean fewer frustrated single and married men turning to prostitutes.
Dearer for johns
Our analysis shows how a prostitute’s hourly rate varies according to the nature of the services she provides and her reported physical characteristics. As in other bits of the economy, clients who seek niche services must pay more. Sex workers who offer anal sex or spanking earn on average $25 or $50 more per hour, respectively (see chart 2). Those who will accept two male clients at once or do threesomes with another woman command a larger premium.
Appearance matters a great deal. The customers who reported encounters to the website we analysed clearly value the stereotypical features of Western beauty: women they describe as slim but not scrawny, or as having long blonde hair or full breasts, can charge the highest hourly rates (see chart 3). Hair that is bleached too unconvincingly to be described as blonde attracts a lower premium, but is still more marketable than any other colour. For those not naturally well endowed, breast implants may make economic sense: going from flat-chested to a D-cup increases hourly rates by approximately $40, meaning that at a typical price of $3,700, surgery could pay for itself after around 90 hours. The 12% share of women featured on the site who are described both as athletic, slim or thin, and as being at least a D-cup, suggests that quite a few have already taken this route.
A prostitute’s rates also vary according to her ethnicity and nationality. What attracts a premium in one place can attract a penalty in another. According to our analysis, in four big American cities and London, black women earn less than white ones (see chart 4).
We had too few data from other cities for a reliable breakdown by ethnicity. But Christine Chin of the American University in Washington, DC, has studied high-end transnational prostitutes in several countries. In Kuala Lumpur, she found, black women command very high rates and in Singapore, Vietnamese ones do. In Dubai, European women earn the most. What counts as exotic and therefore desirable varies from place to place, and depends on many factors, such as population flows.
Local markets have other quirks. According to the site we analysed, an hour with an escort in Tokyo is a bargain compared with one in London or New York. Yet a cost-of-living index compiled by the Economist Intelligence Unit, our sister organisation, suggests that Tokyo is the most expensive city overall of the three. The apparent anomaly may be because escorts who appear on an English-language review site mostly cater to foreigners, who are not offered the more unusual—and expensive—services Japanese prostitutes provide for locals. These include the bubble baths and highly technical massages of Sopurando (“Soapland”), a red-light district in Tokyo, which can cost ¥60,000 ($600) for a session and involve intercourse (although that is not advertised).
A degree appears to raise earnings in the sex industry just as it does in the wider labour market. A study by Scott Cunningham of Baylor University and Todd Kendall of Compass Lexecon, a consultancy, shows that among prostitutes who worked during a given week, graduates earned on average 31% more than non-graduates. More lucrative working patterns rather than higher hourly rates explained the difference. Although sex workers with degrees are less likely to work than others in any given week (suggesting that they are more likely to regard prostitution as a sideline), when they do work they see more clients and for longer. Their clients tend to be older men who seek longer sessions and intimacy, rather than a brief encounter.
How much brothels and massage parlours use the internet depends on local laws. America’s legal restrictions mean that they keep a low profile, both offline and online. In Britain, where brothels are illegal though prostitution is not, massage parlours advertise the rotas and prices of their workers online but are coy about the services rendered. By contrast Paradise, a mega-brothel in Germany, boasts a frank and informative website.
But it is independent sex workers for whom the internet makes the biggest difference. Mr Cunningham has tracked the number of sex workers in American cities on one review site. In the decade to 2008, during which online advertising for commercial sex took off, the share describing themselves as independent grew.
For prostitutes, the internet fulfils many of the functions of a workplace. It is a “break-room and hiring hall”, says Melissa Gira Grant, the author of “Playing the Whore: The Work of Sex Work”. Online forums replace the office water-cooler. Women exchange tips on dealing with the everyday challenges of sex work; a busy thread on one forum concerns which sheets stand up best to frequent washing.
A mother in Scotland asks how other prostitutes juggle child care and selling sex, given that bookings are often made at short notice so babysitters are hard to arrange. Another contributor who is thinking of having children asks how much other women saved before taking time off to have a baby, and whether the new calls on their time meant they earned less after giving birth. One reply points out that prostitution is easier than many other jobs to combine with motherhood: it pays well enough to cover child-care costs, and can be fitted around school holidays, plays and sports days, and children’s illnesses.
Women who are considering entering the industry often seek advice online from those already in it before making up their minds. Melanie, who earns £65,000 ($109,000) a year, says that she is considering selling sex on the side for a few months to pay off debts. She asks which agency to use and how to get the highest rate. But she also worries that a stint selling sex would harm her future career. Experienced sex workers respond that anonymity will be easier to preserve if she works independently, rather than through an agency, and warn her that she is entering a crowded market. The stress of living a double life should not be underestimated, they caution, and it will not be easy money.
Many of those contributing to such discussions hold other jobs, often part-time, and tout the merits of a steady source of additional income and something innocuous to put on a CV. Sarah says her escort work means she can pay for her daughter’s dance and music lessons, which would be unaffordable on just her “civvy job”. Some husbands and boyfriends know about their wives’ and girlfriends’ work, or even act as managers, drivers and security. Other women keep what they do a secret from those closest to them.
Advertising and booking clients online give prostitutes flexibility about where to work. They can “tour”, using their own home pages or profiles on specialist websites to advertise where they will be and when. In densely populated Britain, where prostitutes work in most places, tours allow those who normally serve small towns to visit cities crammed with potential customers. In Norway, says Ms Skilbrei, prostitutes are concentrated in the main cities, so a tour is a chance to satisfy pent-up demand in small towns.
The freelancers, part-timers and temps the internet is bringing to the sex trade are likely to help it absorb demand shocks. In 2008 the Republican and Democratic national conventions were held in Minneapolis and Denver respectively. Around 50,000 visitors flocked to each city. Another study by Mr Cunningham and Mr Kendall found that the numbers of advertisements for sex on the now-defunct “erotic services” section of Craigslist, a classified-advertising site, were 41% higher in Minneapolis and 74% higher in Denver around the conventions than expected for those days of the week and times of year.
Health and safety
Sex work exposes those who do it to serious risks: of rape and other violence, and of sexually transmitted infections. But in this industry, like many others, the internet is making life easier.
Online forums allow prostitutes to share tips about how to stay safe and avoid tangling with the law. Some sites let them vouch for clients they have seen, improving other women’s risk assessments. Others use services such as Roomservice 2000, another American site, where customers can pay for a background check to present to sex workers. Both sides benefit since the client can demonstrate trustworthiness without giving credit-card details or phone numbers to the prostitute.
Sites that are active in restrictive jurisdictions must be careful not to fall foul of the law. In June the FBI shut down MyRedBook, an advertising-and-review site with a chat section for sex workers. Its owners face charges of money laundering and facilitating prostitution. American police sometimes use such sites to entrap prostitutes. As they wise up to this, sex workers are using sites that allow them to verify clients’ identities to help them avoid stings. But that adds unnecessary hassle and distracts from what should be most important: staying safe. “Screening for cops [is now] the priority over screening for rapists, thieves, kidnappers,” says Ms Doogan.
In Britain, Ugly Mugs runs an online database that prostitutes can use to check punters’ names and telephone numbers. In America the National Blacklist, a “deadbeat registry”, allows them to report men who are abusive or fail to pay. Other women can check potential clients by names, telephone numbers, e-mail addresses and online aliases. Though not specifically aimed at sex workers, apps such as Healthvana make it easy for buyer and seller to share verified results in sexual-health tests.
Moving online means prostitutes need no longer rely on the usual intermediaries—brothels and agencies; pimps and madams—to drum up business or provide a venue. Some will decide to go it alone. That means more independence, says Ana, a Spanish-American erotic masseuse who works in America and Britain. It also means more time, effort and expertise put into marketing. “You need a good website, lots of great pictures, you need to learn search-engine optimisation…it’s exhausting at times,” she says.
Leaving the streets behind
Others will still prefer to have a manager or assistant to take care of bookings and social media. “[Nowadays] you have people hitting you up on Twitter, Facebook, your website, and e-mail,” says Ms Doogan. Eros.com, an international listings site, allows prostitutes to tell clients whether they are currently available. But it means going online every hour or two, which is a chore. And online advertising is not cheap. Ms Doogan used to spend 10% of her income on print adverts; she spends far more on online ones because with so many people advertising, returns are lower. Checking customers’ bona fides also takes time.
Meanwhile some traditional forms of prostitution are struggling. In the decade to 2010 the number of licensed sex clubs in the Netherlands fell by more than half, according to a study for Platform31, a Dutch research network. Much of the decline will have been offset by the growth of sex work advertised online, it reckons. Many prostitutes would rather work from private premises than in a club or for an agency, says Sietske Altink, one of the authors. Dutch municipalities often bar such work—but the option of finding clients online makes such rules harder to enforce.
That shift will make the sex industry harder for all governments to control or regulate, whether they seek to do so for pragmatic or moralistic reasons, or out of concern that not all those in the industry are there by their own free will. Buyers and sellers of sex who strike deals online are better hidden and more mobile than those who work in brothels, or from clubs or bars, points out Professor Weitzer of George Washington University. Ireland has banned the advertising of sexual services since 1994. The prohibition has achieved almost nothing, says Graham Ellison, a sociologist at Queen’s University in Belfast. Websites simply moved to other jurisdictions. The closure of those such as MyRedBook may prompt American ones to do the same; as they grow more specialised, the excuse that they merely host classified advertisements is wearing thin.
In the long term there will always be people who, for whatever reason, want to hire a prostitute rather than do without sex or pick up a partner in a bar. As paid-for sex becomes more readily and discreetly available online, more people will buy it. A greater awareness may develop that not all sex workers are the victims of exploitation. The very discretion—and the hidden nature of such prostitution—may also mean that the stigma persists. But, overall, sex workers will profit. The internet has disrupted many industries. The oldest one is no exception.
www.economist.com/news/briefing/21611074-how-new-technology-shaking-up-oldest-business-more-bang-your-buck]http://www.economist.com/news/briefing/21611074-how-new-technology-shaking-up-oldest-business-more-bang-your-buck[/url]



